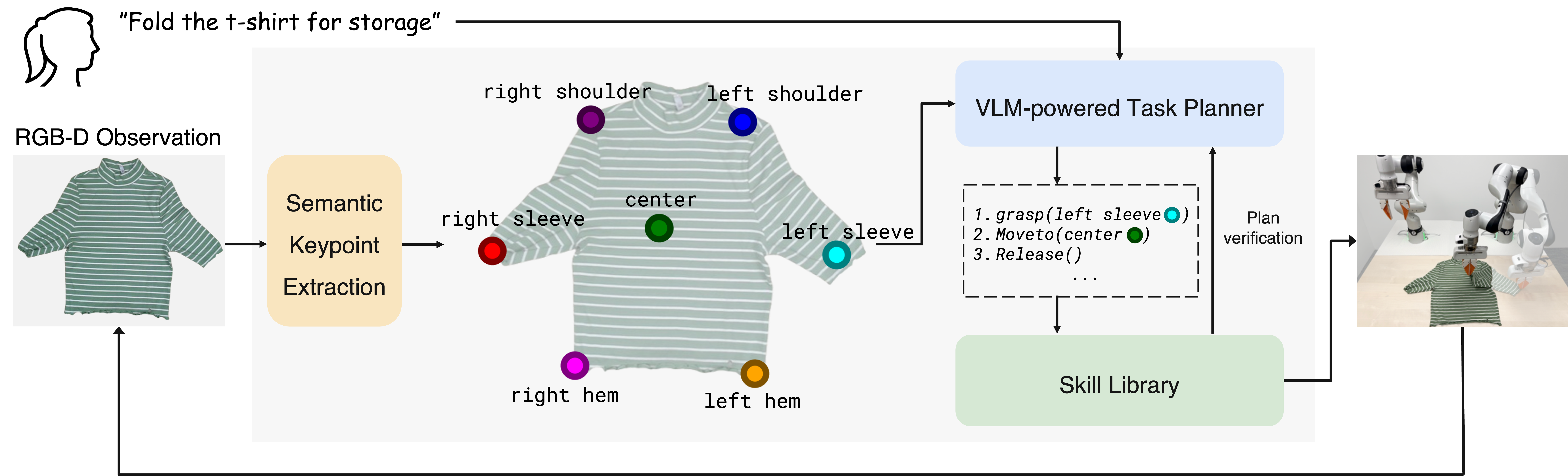
Semantic Keypoints
Inspired by the way humans manipulate clothes, we introduce semantic keypoints as a general spatial-semantic representation of clothes. These keypoints carry explicit semantic meaning, can be described using natural language, and provide a sparse yet succinct representation. As a result, they are easy to extract from visual observations, generalize well across different clothes instances, and effectively define affordances for manipulation.

CLASP
CLASP overview. Given an RGB-D observation, CLASP extracts semantic keypoints as the state. These keypoints, along with the RGB image and task instruction, are fed to a VLM to generate a sub-task sequence. Once verified, the sub-tasks are executed. After each sub-task, CLASP updates the observation and decides whether to replan. This loop continues until the task is complete.
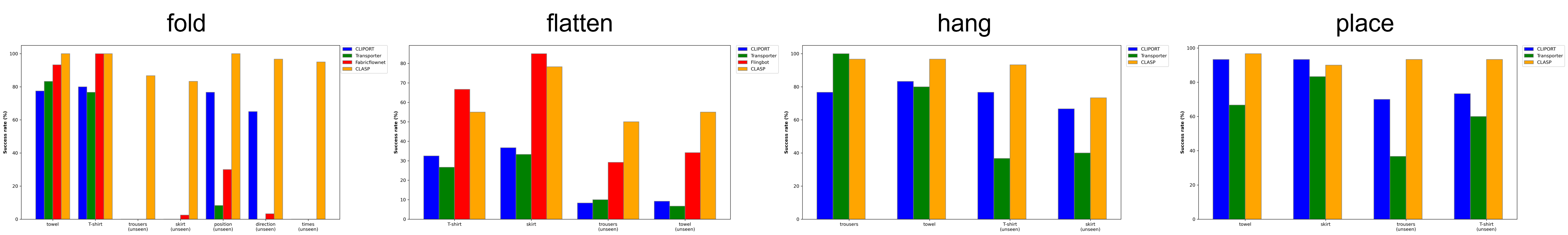
Results
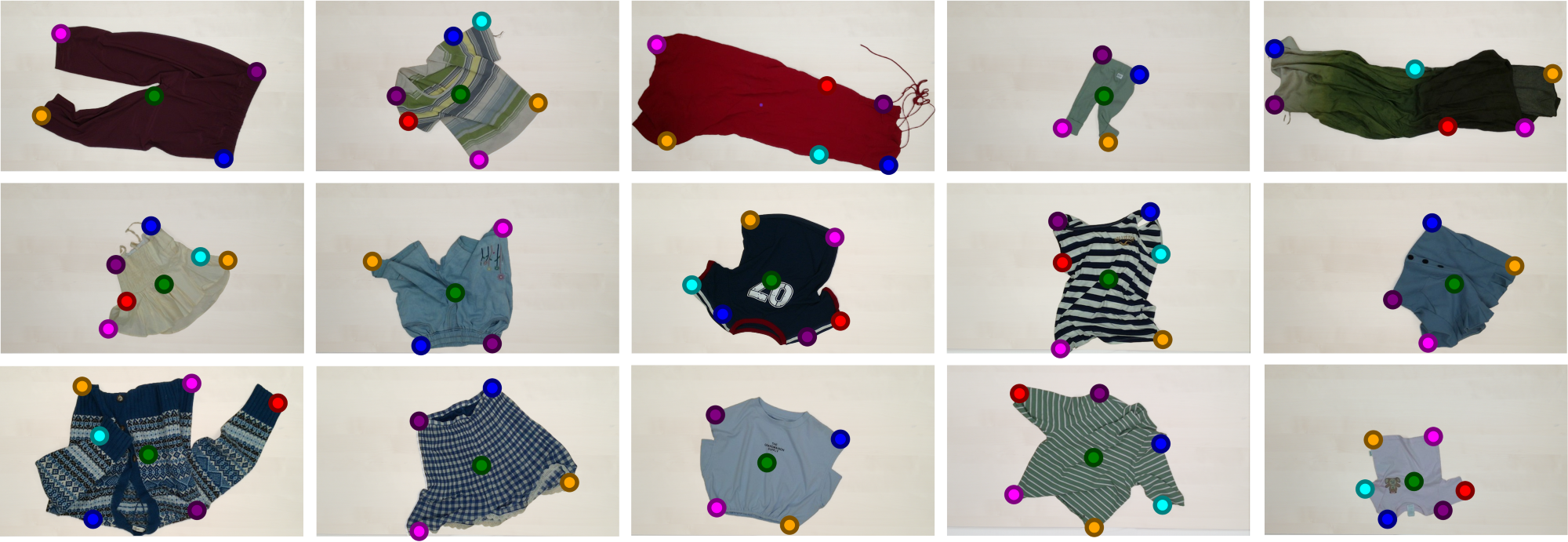
Semantic Keypoints Extraction
Our method can achieve open-category semantic keypoint extraction under irregular deformation and occlusion.

BibTeX
@article{deng2025clasp,
title = {CLASP: General-Purpose Clothes Manipulation with Semantic Keypoints},
author = {Yuhong Deng and Chao Tang and Cunjun Yu and Linfeng Li and David Hsu},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2507.19983},
year = {2025},
}